Once the user is created, go to the Oracle Cloud Services under Identity domains and choose the OIC instance which was created earlier.
Blog About Oracle Cloud, Oracle EBS 12.2 upgrade, Database 19c upgrade, cloud solutions, IaaS, PaaS, Cloud, Lift and shift to Oracle Cloud and day to day Oracle Issue... Mostly.
Thursday, April 25, 2024
Mastering Oracle Cloud: Step-by-Step Guide to Provision Your OIC Instance
Once the user is created, go to the Oracle Cloud Services under Identity domains and choose the OIC instance which was created earlier.
Tuesday, April 23, 2024
Strengthen Your Cloud Security: Exploring OCI Vulnerability Scanning Services
In this post, we are going to explain, once a CVE is detected, then what is the approach we can take to mitigate those CVE risks. But before we do so, i would suggest we go through the official Oracle Documentations VSS.
Server was already having the version 4.5.0-36.el7_9.5
rpm -qa|grep libvirt
Steps:
Steps:-
1.
cd /etc/yum.repos.d
2.
took the backup of file public-yum-ol7.repo
3.
took the backup of boot volume
4.
in the file public-yum-ol7.repo, enabled the
flag as 1 for section
1.
Reboot the server
2.
Disable and enable VSS
3.
Verify the Scanning report
4.
Check with the application team for sanity
before moving it to next higher instances
These are the many ways through which we can mitigate the CVEs being reported by VSS in OCI. I hope this post will help someone. Till then, happy learning cloud.
Monday, April 8, 2024
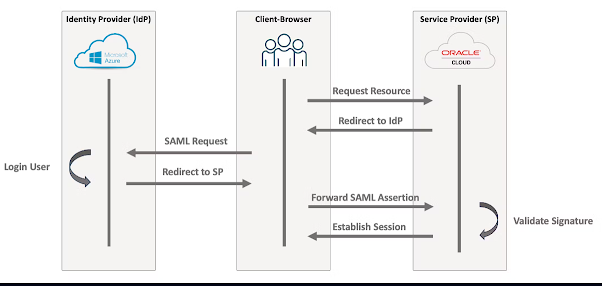
Cross-Platform Efficiency: Mastering Federation of Azure AD with OCI Identity Domains for SSO Solution
Thursday, April 4, 2024
Secure Your Network: Private DNS in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Key features and benefits of Private DNS in OCI include:
Custom Domain Names: You can create your own domain names, such as example.com or subdomain.example.com, tailored to your organization's needs.
Resource Mapping: Private DNS allows you to map these custom domain names to specific resources within your VCN, making it easier to manage and access your services.
Network Isolation: By using Private DNS within your VCN, you can ensure that your domain names remain private and are only accessible within your network, enhancing security and control.
Integration with Oracle Services: Private DNS seamlessly integrates with other Oracle Cloud services, enabling you to easily manage domain names for resources such as Compute instances, Load Balancers, and more.
Automation and Scalability: You can automate the creation and management of domain names using OCI's APIs, CLI, or Terraform, making it easy to scale and manage your infrastructure.
Overall, Private DNS in OCI provides a flexible and secure way to manage domain names and map them to resources within your virtual cloud network, facilitating efficient communication and management of your cloud infrastructure.
Now, the objective of this post is to give an idea on how we can communicate to the resources using their hostnames. As we know, DNS is a feature which translates hostnames to IP addresses. If we have resources in OCI and they don't know the respective hostnames, then the communication can't be established. To mitigate this problem, OCI has the option of Private DNS in OCI.
A small use case here.
When we provision a compute instance, it comes with its own fully qualified domain name example oraclevcn.com. Now, if i need to set it to samappsdba.com, we need to perform some additional steps.
The high level steps
Private DNS Zone – which contain DNS data from the VCN (like IP address)
Private DNS Views – this is collection of Zones, Zone can only belong to a single View.
Private DNS Resolver – you can assign Views to Resolver which will then resolve those DNS queries for you. Remember the order, first custom views, then default and finally from Internet
[opc@instance-20240328-1959 ~]$ host -t NS samapspdba.com
samapspdba.com name server vcn-dns.oraclevcn.com.
[opc@instance-20240328-1959 ~]$
After I delete it the private view
@instance-20240328-1959 ~]$ host -t NS samapspdba.com
samapspdba.com name server vcn-dns.oraclevcn.com.
[opc@instance-20240328-1959 ~]$ nslookup www.samapspdba.com
Server:
169.254.169.254
Address:
169.254.169.254#53
** server can't find www.samapspdba.com: REFUSED
This is a basic demonstration on how using private DNS feature in OCI, we can customize the hostname.
I hope this post helps someone.